Information gain is a very important concept in information theory. In the most simplest case, it is the reduction in entropy. If you are not familiar with entropy, check out my entropy post. Information gain is used in decision trees. A decision tree is a classification algorithm. Decision tree splits the given feature from specific points with specific questions by branching. By doing that, it tries to maximize information gain. In other words, it tries to minimize the entropy in each branch. To sum up, information gain tells us the reduction in entropy in each split.
Let’s clear out this concept with a simple example.
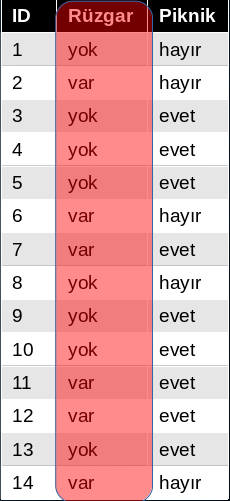
The above toy dataset contains 14 samples of wind measurements and their
respected picnic/no-picnic records. The first thing to do is to find the how
much information does Picnic column have. There is 9 Evet and 5 Hayır
records, total of 14 measurements. Thus, the entropy of Picnic variable is
following.
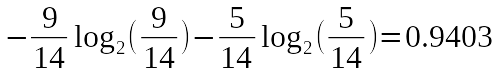
Now, if we split the Picnic variable by the wind situation var/yok, the
average reduction in the entropy would be the information gain. To do that,
let’s put the Evet and Hayır measurements next to each other in a row, and
split it by the wind measurements.
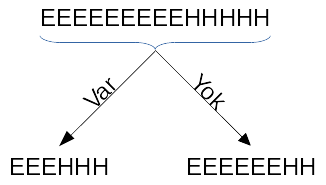
Here, we should find the entropy in each leaf node. Then, we are going to calculate the weighted average of entropy by taking account of the E/H count in each node.
In the left most leaf node, the entropy is 1 since picking a letter results with the probability of 0.5 of E and 0.5 of H. For the right node, we can calculate the entropy as follows.
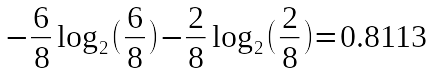
Now, we can calculate the weighted average of entropy. There is 6 samples in the left, and 8 samples in the right. The following equation calculates the weighted average.
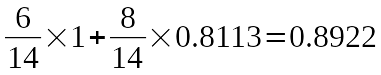
The last part is the calculating the reduction in the entropy. We just need to extract the average entropy from the first one.
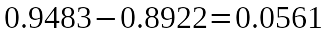
This result tells us if we split the Picnic variable by the wind situations,
there will be a 0.0561 reduction in the entropy. In another words, there will be
a 0.0561 of information gain in this split.
In a decision tree, we do that for all of the independent variables. We calculate the each individual information gain for all of the independent variables. Then, we choose the feature that causes the largest reduction in entropy and split the tree into branches. We continue to the process until there is no split to make (entropy is 0) or to meet a stop condition (maximum split count or maximum depth of the tree). There are multiple ways to calculate the information gain for different purposes. Information gain is only one of them. Maybe, in another post I will write about some of them. Until then, see you in another day. Bye…


